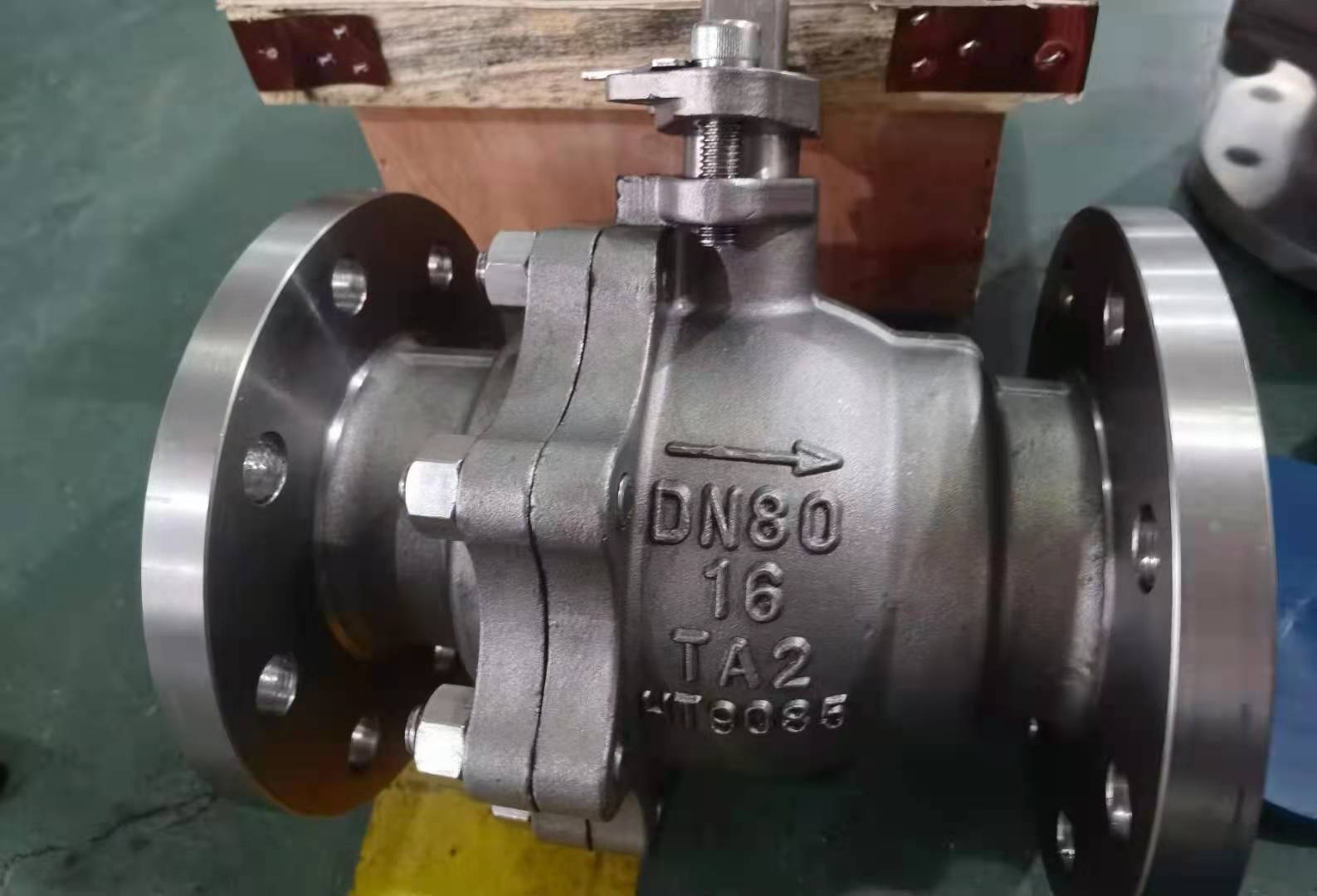
duplex stainless steel Ball Valve F51 4A CD3MN S31803 2205
duplex stainless steel Ball Valve is a kind of valve that can be opened and closed by rotating the ball around the center line of the valve body. The sealing element is embedded in the valve seat. A spring is set at the end of the metal valve seat. When the sealing surface is worn or burned, the valve seat and the ball are pushed to form a metal seal under the action of the spring. It has the function of automatic pressure relief. When the medium pressure in the valve cavity exceeds the spring preload, the valve seat at the outlet end retreats away from the ball to achieve the effect of automatic pressure relief. After pressure relief, the valve seat automatically resets. It is suitable for water, solvent, acid, natural gas and other general working media, but also for media with poor working conditions, such as oxygen, hydrogen peroxide, methane and ethylene. It is widely used in various industries.
Structural features of natural gas worm gear ball valve:

China duplex stainless steel Ball Valve Supplier,China duplex stainless steel Ball Valve Manufacture,duplex stainless steel Ball Valve Factory
1. Valve seat sealing structure
The valve seat adopts the front sealing design structure, which has the functions of two-way sealing and automatic pressure relief in the middle chamber. The seal seat embedded with sealing materials is floating, which is loaded by the spring. When in the closed position, the sealing surface always keeps close contact with the ball to ensure that the valve can achieve leakage sealing under high and low pressure differences.
2. Automatic pressure relief structure
When the pressure in the middle chamber rises abnormally, the ball valve with single seal structure has the function of automatic pressure relief, while the ball valve with double seal structure has additional pressure on the valve body
3. Sealed emergency rescue function
The valve is designed with auxiliary valve seat emergency sealing system. Once the sealing surface is damaged, the corresponding sealant can be injected into the auxiliary sealing system for emergency rescue, and the valve seat area can also be flushed and lubricated through the auxiliary system when necessary.
4. Anti static device
When operating the valve, electrostatic charges will be generated and accumulated in the ball line due to friction between the ball seats. In order to prevent electrostatic sparks, anti-static devices are specially set on the valve to export the generated static electricity (please contact our salesman for detailed instructions).
5. Fireproof structure
The fixed ball valve seat of our company adopts the structure. In case of fire, when the non-metallic sealing surface material is burned, the metal ring uses the spring force to push the valve seat and the ball to fit and seal, so as to prevent the spread of fire and the outflow of media. (The fire protection structure design shall comply with API607, JB/T6899 and BS755)
6. Full bore structure and reduced bore structure
In order to meet the needs of users, our company has full bore ball valves and reduced bore valves. The pipe inner diameter of full bore ball valves is consistent with the pipe inner diameter, which is easy to clean. The reduced bore ball valves are light in weight, and their fluid resistance is only a part of the same caliber globe valves, which has a broad prospect.
7. Discharge device of valve body
The drain valve can be installed on the valve body of the ball valve according to the requirements of the customer. Once both ends of the valve are closed, the accumulated pressure in the valve chamber can be discharged through the drain valve of the valve body.
8. Extended valve rod device (optional)
For buried ball valves, extension devices can be provided, including valve stems, grease injection valves, drain valves, etc. Extended height (length generally refers to the distance from the center of valve channel to the center of operating device)
Standards adopted for natural gas worm valve: GB, ANSI, DIN, JIS
What is the duplex stainless steel?
Duplex stainless steel is a mixed austenitic(50%) and ferrite(50%) in view of microstructure, the special structure bring it better performance of strength and corrosion resistance to the origin austenitic stainless steel or ferrite.
The duplex stainless steel has a big family of name and codes. in ASTM grade, it varies from A890/A990/A995 1A, 1B, 1C to 4A, 5A, 6A, 7A; in UNS Numbers, it is called S31803, S32750, S32760 etc; in ASTM Number, it is A998 CD6MN, CD3MN, CE3MN etc; in forging equivalent, it is A182-F51, F53, F55 etc; in common name, it is duplex 2205, super duplex 2507 etc; and in European material codes, it is DIN1.4462, 1.4410, 1.4501 etc;
What is the benefits the duplex steel bring?
Similar corrosion resistance to SS316
Greater tensile and yield strength
Good ductility and toughness
Good stress corrosion cracking resistance (SSC)
What is the applications the duplex steel used in?
Petrochemical
Desalination plants
Chemical processing and transportation
Chloride-handling industries
Valve stems
Equivalent grades:
| ASTM GRADE | A990-1A | A990/A995-1B | A990-1C | A990/A995-2A | A990/A995-3A | A990/A995-4A | A990/A995-5A | A990/A995-6A | A990/A995-7A | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | 25Cr5NiMoCu | 25Cr5Ni2Mo3Cu | 25Cr6NiMoCuN | 24Cr10Ni4MoV | 25Cr5NiMoV | 22Cr5Ni3MoN | 25Cr7Ni4MoN | 25Cr7Ni3.5MoWCb | 27Cr7Ni-Mo-W-N | 25Cr7Ni3.5MoWCb |
| UNS No. | J93370 | J93372 | J93373 | J93345 | J93371 | S31803/S32205 | S32750 | S32760 | S31254 | |
| ASTM No. | A995-CD4MCuN | A995 CD4MCu | A351-CD3MCuN* | A351-CE8MN/ CD3MCuN | A351-CD6MN | A995 CD3MN | A351-CE3MN | A995 CD3MWCuN | A351-CD3MWN | A351-CK3MCuN |
| Forged Equiv. | A182-F50* | F61* | A182-F51 | A182-F53 | A182-F55 | (Zeron 100TM) | A182-F44 | |||
| Common Name | Duplex | Duplex | Duplex | Duplex | Duplex | Duplex 2205 | Super Duplex 32750 | Super Duplex | Super Austenitic/Duplex | Super Duplex |
| European (DIN) | 1.4462 | 1.4410 | 1.4501 | UNS J93379 |
Applications:
| FORGING SPECIFICATION | COMMON DESIGNATION | ASTM CAST | WROUGHT BAR SPECIFICATION | SERVICE RECOMMENDATIONS (1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM A182 F44 | 20% Chrome; 18% Nickel; 6% Mo; 0.25% C Super Stainless Steel | ASTM A351 Grade CK3MCuN (A995-1B) Super Austenitic | ASTM A479 S31254 | (2.54 SMO) Acetic acid, antibiotics and drugs, bleaching compounds, formic acid, fruit and juices, hot air, hot water, hydrocarbons, hydrochloric acid, organic liquids and acids, nitric acid, organic salts, oxalic acid, phosphoric acid, sea water, sewage, sodium bisulfite, steam, sulfamic acid, 10% sulfuric acid. |
| ASTM A182 F50 | 25.5% Chrome; 5.5% Nickel; 2% Mo; 0.040% C Super Stainless Steel | ASTM A351 Grade CD4MCu (A995-1A) | ASTM A479 S32550 | Concentrate brine, fatty acids, potable water, pulp water, pulp liqurs at 220ºF (104ºC), sea water, steam, sulfuric acid (15-30% @ 140-160ºF (60-71ºC), sulfuric acid (35-40% @ 185ºF (85ºC), plus 5% organics). |
| 24% Chrome; 9.5% Nickel; 4% Mo; 0.080% C Duplex Stainless Steel | ASTM A351 Grade CE8MN (A995-2A) | Concentrate brine, fatty acids, potable water, pulp water, pulp liqurs at 220ºF (104ºC), sea water, steam, sulfuric acid (15-30% @ 140-160ºF (60-71ºC), sulfuric acid (35-40% @ 185ºF (85ºC), plus 5% organics). | ||
| ASTM A182 F51 | 22% Chrome; 5% Nickel; 3% Mo; N; 0.030% C Duplex Stainless Steel | ASTM A351 Grade CD3MN (A995-4A) | ASTM A479 S31803** | Concentrate brine, fatty acids, potable water, pulp water, pulp liqurs at 220ºF (104ºC), sea water, steam, sulfuric acid (15-30% @ 140-160ºF (60-71ºC), sulfuric acid (35-40% @ 185ºF (85ºC), plus 5% organics). |
| ASTM A182 F53 | 25% Chrome; 7% Nickel; 4.5% Mo; N; 0.030% C Duplex Stainless Steel Grade 5A | ASTM A995 Grade CE3MN (A995-5A) | Concentrate brine, fatty acids, potable water, pulp water, pulp liqurs at 220ºF (104ºC), sea water, steam, sulfuric acid (15-30% @ 140-160ºF (60-71ºC), sulfuric acid (35-40% @ 185ºF (85ºC), plus 5%organics). Useful where the Pitting Resistance Number (PREN) is required. | |
| ASTM A182 F55 | 25% Chrome; 7.5% Nickel; 3.5% Mo; N; 0.030%} C Duplex Stainless Steel Grade 6A | ASTM A995 Grade CD3MWCuN (A995-6A) | Concentrate brine, fatty acids, potable water, pulp water, pulp liqurs at 220ºF (104ºC), sea water, steam, sulfuric acid (15-30% @ 140-160ºF (60-71ºC), sulfuric acid (35-40% @ 185ºF (85ºC), plus 5% organics). Useful where the Pitting Resistance Number (PREN) is required. |
Material chemical composition:
| UNS S31803/A182 F51/1.4462 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Cr | Mn | Mo | N | Ni | P | S | Si |
| 0.030 | 21.0- | 2.00 | 2.50- | 0.08- | 4.50- | 0.030 | 0.020 | 1.00 |
| max | 23.0 | max | 3.50 | 0.20 | 6.50 | max | max | max |
| UNS S32205 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Cr | Mn | Mo | N | Ni | P | S | Si |
| 0.030 | 22.0- | 2.00 | 3.00- | 0.14- | 4.50- | 0.030 | 0.020 | 1.00 |
| max | 23.0 | max | 3.50 | 0.20 | 6.50 | max | max | max |
We produce duplex stainless steel ball valves,2205 Dual Plate Check Valve,CD3MN Swing Check Valve,ASTM B367 GR.C2 Titanium Swing Check Valve,150LB CN7M Globe Valve,150LB CN7M Gate Valve.